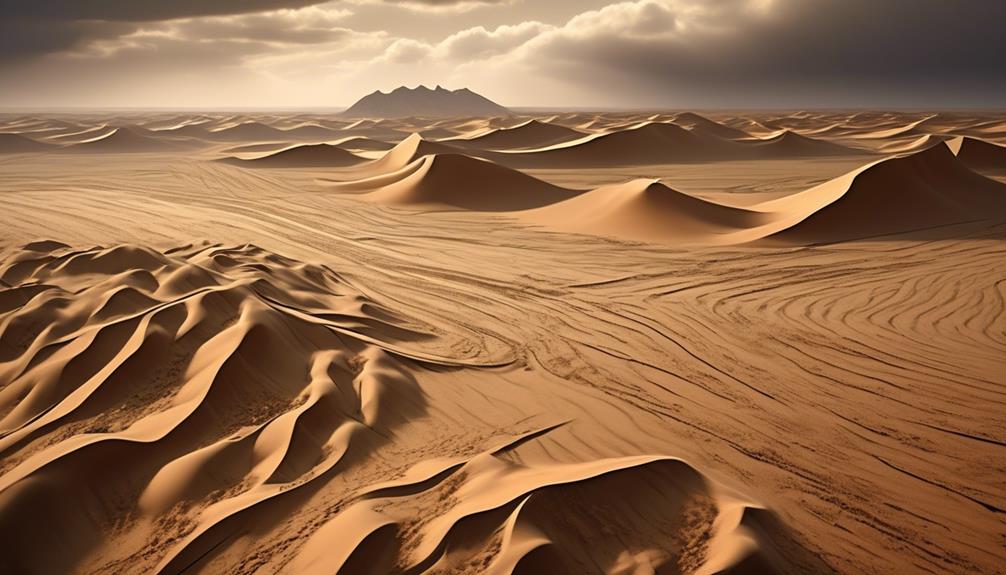
Regarding wind erosion, it’s common to imagine soil particles perpetually touching the earth, but have you considered the particular kind of wind erosion where this happens? Grasping the intricacies of this phenomenon is essential for realizing its effects on soil health and environmental conditions.
Join us as we explore the factors influencing soil particle movement, the implications of wind erosion on land and vegetation, and strategies for mitigating soil displacement.
Key Takeaways
- Wind erosion occurs when soil particles are in constant contact with the ground.
- Dry, sandy soils or loose, dry, and finely granulated soils are particularly susceptible to wind erosion.
- Wind erosion can lead to significant degradation and reduced fertility of the soil, impacting agricultural yields and ecosystem stability.
- Implementing strategies such as vegetation preservation, ground cover, soil moisture management, and erosion control structures is crucial for mitigating soil particle displacement caused by wind erosion.
Defining Soil Particles in Constant Contact
When soil particles are in constant contact with the ground, they become highly susceptible to wind erosion. This type of erosion, known as deflation, occurs when the force of the wind causes the soil particles to be lifted and carried away. It primarily affects dry, sandy soils or loose, dry, and finely granulated soil where the particles are constantly in contact with the ground. Understanding the behavior of soil particles in these conditions is crucial for effective erosion control.
In the context of wind erosion, soil particles in constant contact with the ground can lead to significant challenges in maintaining soil quality and preventing land degradation. Factors such as soil moisture, wind speed, soil particle size, ground cover, and physical barriers play a crucial role in influencing the extent of wind erosion. Managing these factors is essential for preserving soil fertility and preventing the negative impacts of wind erosion on agricultural productivity and environmental sustainability.
Impact of Wind Erosion on Soil Quality

Impact of Wind Erosion on Soil Quality can be severe, leading to significant degradation and reduced fertility.
Wind erosion has detrimental effects on soil physical properties, which are essential for supporting plant growth and maintaining soil health. The abrasive action of wind-blown particles can lead to soil compaction, reduced water infiltration, and increased susceptibility to water erosion.
Additionally, the loss of topsoil through wind erosion can deplete the soil of organic matter and nutrients, diminishing its ability to sustain healthy plant growth. As a result, wind-eroded soils may exhibit decreased fertility and productivity, impacting agricultural yields and ecosystem stability.
Furthermore, the exposure of bare soil due to wind erosion can exacerbate the loss of valuable soil through subsequent erosion processes.
Therefore, it's crucial to implement soil conservation practices, such as windbreaks, cover crops, and reduced tillage, to mitigate the detrimental impact of wind erosion on soil quality and preserve the long-term productivity of agricultural lands.
Factors Influencing Soil Particle Movement
Factors influencing the movement of soil particles include wind speed, soil moisture, soil particle size, ground cover, and physical barriers.
- Wind Speed: Higher wind speeds increase the force exerted on soil particles, leading to more significant movement.
- Soil Moisture: Dry soils are more susceptible to wind erosion as they lack cohesion, making it easier for particles to be lifted and transported by the wind.
- Soil Particle Size: Smaller particles are more easily lifted and transported by the wind compared to larger ones.
- Ground Cover: The presence of vegetation or other forms of ground cover can shield soil particles from direct wind impact, reducing the likelihood of erosion.
In the context of wind erosion, these factors play a crucial role in determining the extent and severity of soil particle movement.
Understanding these influences is essential for implementing effective soil conservation measures and mitigating the adverse effects of wind erosion. By considering wind speed, soil moisture, particle size, and ground cover, it's possible to develop strategies that minimize soil particle movement and the associated detrimental impacts on agricultural productivity and environmental sustainability.
Understanding the Dynamics of Wind Erosion

Understanding the dynamics of wind erosion builds upon the foundational knowledge of factors influencing soil particle movement, emphasizing the constant contact between soil particles and the ground in the process.
Wind erosion, a natural process, involves the continuous interaction between soil particles and the ground, facilitating soil transportation and deposition. This process encompasses various types of wind erosion, such as surface creep, saltation, and suspension, which are influenced by factors like soil moisture, wind speed, particle size, ground cover, and physical barriers.
Human activities, including land clearing, over-grazing, and vegetation removal, can exacerbate wind erosion, leading to decreased cropland productivity and impairment of soil properties. Wind erosion is particularly prevalent in dry, sandy soils or loose, dry, and finely granulated soils, often causing environmental degradation in windy areas.
The impacts of wind erosion extend beyond local soil disturbance, contributing to global environmental degradation and accelerated erosion due to the absence of protective vegetation cover. Therefore, understanding the dynamics of wind erosion is crucial for implementing effective soil conservation strategies and mitigating the detrimental effects of this natural process.
Mitigating Soil Particle Displacement
To reduce soil particle displacement caused by wind erosion, incorporating vegetation as physical barriers can effectively mitigate the impact on soil stability and cropland productivity. This approach helps keep the soil in place, preventing erosion and maintaining its fertility. Additionally, implementing water management techniques can further stabilize the soil, making it less susceptible to displacement by wind.
Here are four key strategies for mitigating soil particle displacement:
- Vegetative Barriers: Planting trees and shrubs as windbreaks can shield the soil from the erosive forces of wind, reducing the likelihood of soil particle displacement.
- Ground Cover: Utilizing crops or grass as ground cover can create a protective layer, minimizing the exposure of soil particles to wind erosion.
- Soil Moisture: Increasing soil moisture levels through proper irrigation and water management practices can enhance soil stability, making it less prone to displacement during wind events.
- Erosion Control Structures: Implementing physical structures such as terraces and contour barriers can help prevent soil particle displacement and mitigate the impacts of dust storms on cropland.
Frequently Asked Questions
During Which Type of Wind Erosion Are Particles in Constant Contact With the Ground?
Deflation is the type of wind erosion where soil particles are in constant contact with the ground. It occurs in dry, sandy soils or loose, dry, and finely granulated soil. Factors like soil moisture, wind speed, soil particle size, ground cover, and physical barriers contribute to deflation.
Causes of deflation include land clearing, over-grazing, and improper land preparation. These activities disturb the soil surface and remove vegetation, making the soil more susceptible to wind erosion.
The impacts of deflation are significant. It can lead to decreased cropland productivity, as the topsoil, which is rich in nutrients and organic matter, is blown away. Additionally, deflation can impair soil properties, such as reducing its ability to retain water and increasing its susceptibility to erosion.
What Is the Erosion of Soil by Wind Called?
Wind erosion, also known as aeolian erosion, is the process of soil being carried away by the wind. It's a natural force that shapes our environment, but human activities can exacerbate it. Factors like soil moisture, wind speed, and ground cover influence its intensity.
Aeolian erosion can lead to desertification and loss of fertile soil, impacting ecosystems and agriculture. Understanding and managing this process is crucial for sustainable land use and conservation.
What Are the Three Types of Wind Erosion?
Sure!
Saltation, suspension, and surface creep are the three types of wind erosion.
Saltation involves soil particles being lifted and bounced along the ground by the wind.
Suspension occurs when very small soil particles are carried high into the air by strong winds.
Surface creep, on the other hand, involves soil particles being in constant contact with the ground.
These processes have significant impacts on cropland productivity and soil properties.
What Are the Soil Particles Movement Due to Wind Erosion?
Soil particles movement due to wind erosion involves bouncing or leaping close to the ground. This occurs during saltation, a type of wind erosion. It causes sand-sized particles to move in a series of short bounces or hops along the ground.
Suspension, another form of wind erosion, lifts very fine soil particles high into the air, carrying them for long distances.
Wind erosion occurs in dry, sandy soils or loose, dry, and finely granulated soils due to the constant impact of wind.
Conclusion
In conclusion, wind erosion, like a relentless dancer, keeps soil particles in constant contact with the ground. This constant movement can have a significant impact on soil quality and the environment.
By understanding the factors influencing soil particle movement and implementing measures to mitigate wind erosion, we can work towards protecting our land and vegetation from the damaging effects of this natural process.